
KATHMANDU: Merchandise exports fell by 5.1% to Rs 25.09 billion in the first two months of the current fiscal year 2024/25, according to the macroeconomic and financial situation report released by Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB). The exports had decreased by 7.8% in the same period of the previous year.
Exports to India, China and other countries fell by 4.5%, 45.3% and 3.9%, respectively. However, exports of tea, particle board, oil cakes, shoes and sandals, and soybean oil, among others, increased. The exports of cardamom, zinc sheets, palm oil, readymade garments, and herbs, among others, decreased.
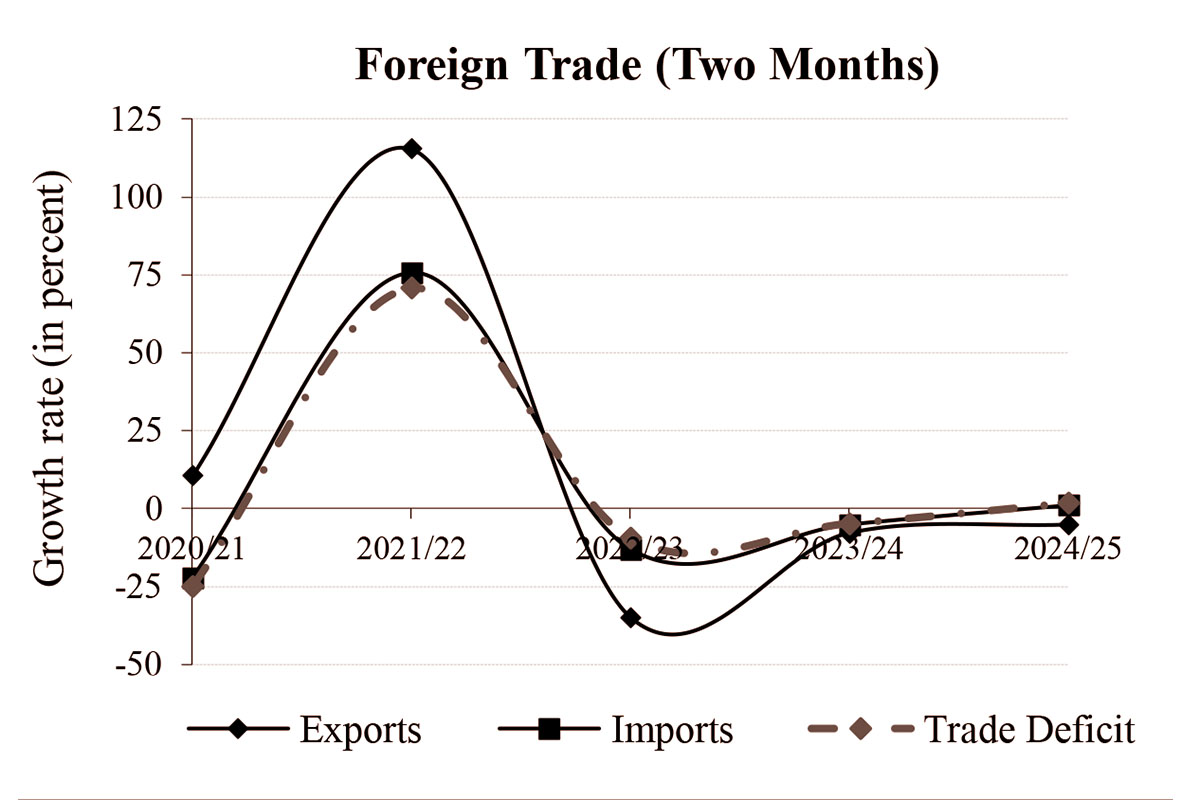
Meanwhile, merchandise imports increased by 1.1% to Rs 262.54 billion, compared to a decrease of 5.1% a year ago. Imports from India and other countries fell by 0.1% and 5.1%, respectively, while imports from China increased by 11.9%. There was an increase in imports of transport equipment, vehicle spare parts, edible oil, chemical fertilisers, telecommunication equipment and parts, and garlic. However, imports of gold, MS billets, rice/paddy, crude palm oil, and electrical equipment decreased during the review period, according to the central bank data.
Exports from Bhairahawa, Dry Port, Kailali, Krishnanagar, and Nepalgunj Customs Offices increased, whereas exports from all other major customs points decreased. On the import side, imports from Bhairahawa, Dry Port, Jaleshwor, Kailali, Mechi, Rasuwa, and Tatopani Customs Offices increased, whereas imports from all other major customs points decreased.
The total trade deficit increased by 1.8% to Rs 237.45 billion during the first two months of 2024/25, compared to a decrease of 4.7% in the corresponding period of the previous year. The export-import ratio decreased to 9.6% in the review period, from 10.2% in the corresponding period of the previous year.
Merchandise imports from India paid in convertible foreign currency amounted to Rs 29.93 billion during the first two months of 2024/25, compared to Rs 32.14 billion in the same period of the previous year.






-1765524551.jpeg)