Coming to grips with the failure of lockdowns is important for several reasons.
Dozens of studies show that lockdowns were an ineffective pandemic response. The list just got longer.
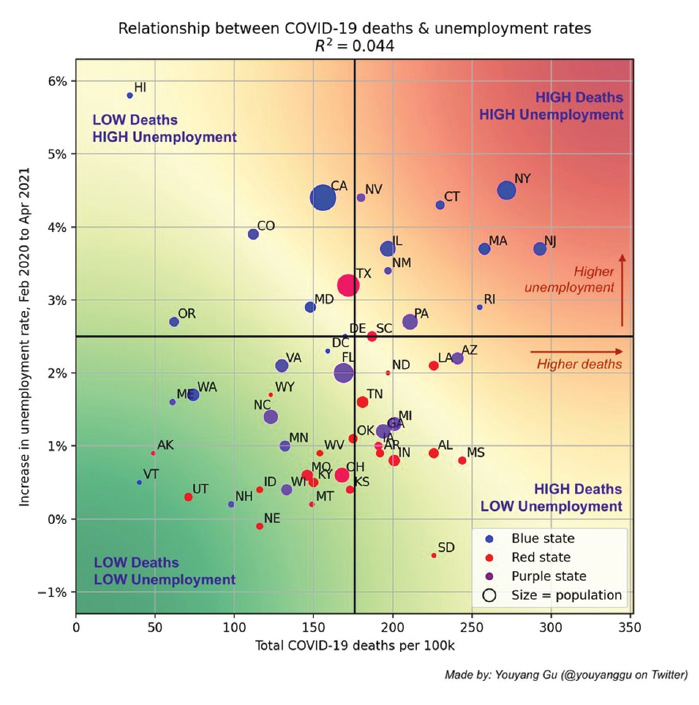
In May, Youyang Gu, an MIT-trained engineer and data scientist, released data showing that government restrictions were not correlated with lower Covid mortality in America. Government restrictions were correlated with higher unemployment, however.
“In the US, there is no correlation between Covid deaths and changes in unemployment rates. However, blue states are much more likely to have higher increases in unemployment,” wrote Gu, the creator of covid19-projections.com, a pandemic modeling site. “More restrictions in a state is NOT correlated with fewer Covid 19 deaths. However, more restrictions is correlated with higher unemployment.”

Recognising the Failure of Lockdowns
The Covid 19 pandemic is finally winding down and more and more people are beginning to acknowledge some hard truths about the failures of the collective response to the virus. George Orwell famously observed that during deceitful times telling the truth is a revolutionary act, so the fact that so many people are finally acknowledging hard truths appears to be a sign we are emerging from deceitful times. For some, such as Dr. Anthony Fauci, these truths are bitter medicine. As Hannah Cox recently observed, Fauci has been on the wrong side of numerous pandemic confrontations with Sen. Rand Paul, and has found himself on the losing end each time. Yet facts are stubborn things. And 14 months after the pandemic’s arrival, we have an abundance of data that shows stay-at-home orders backfired and lockdowns were terribly ineffective at slowing the spread of the virus. The harms of lockdowns, however, are undeniable: economic collapse, millions of jobs and businesses lost, rampant spending, surging debt and poverty, an explosion of drug overdoses, poor mental health, and a collapse of health screenings (including cancer) that will result in hundreds of thousands of excess deaths in the coming years—if not millions. It will not be easy to acknowledge this failure. As The New York Times noted in 2017, humans struggle mightily to admit we were wrong. “Mistakes can be hard to digest, so sometimes we double down rather than face them. Our confirmation bias kicks in, causing us to seek out evidence to prove what we already believe,” wrote Kristin Wong. “The car you cut off has a small dent in its bumper, which obviously means that it is the other driver’s fault.” There’s a name for this psychological phenomenon: cognitive dissonance. “Cognitive dissonance is what we feel when the self-concept — I’m smart, I’m kind, I’m convinced this belief is true — is threatened by evidence that we did something that wasn’t smart, that we did something that hurt another person, that the belief isn’t true,” Carol Tavris, a co-author of the book Mistakes Were Made (But Not by Me), told the Times. Tavris added that cognitive dissonance poses a threat to our sense of self. “To reduce dissonance, we have to modify the self-concept or accept the evidence,” Tavris said. “Guess which route people prefer?”‘Dizzy With Success’
Coming to grips with the failure of lockdowns is important for several reasons. For starters, the pandemic of 2020 will not be the last pandemic Americans face. If we are to avoid the painful experience in the future, we’ll need to better understand how the unorthodox pandemic response came about and determine which public health policies worked and which did not. But there’s an even larger lesson that can be learned. In his Nobel Prize acceptance speech, F.A. Hayek warned of the danger of mankind’s inability to recognise the limits of its knowledge and power.The harms of lockdowns, however, are undeniable: economic collapse, millions of jobs and businesses lost, rampant spending, surging debt and poverty, an explosion of drug overdoses, poor mental health, and a collapse of health screenings (including cancer) that will result in hundreds of thousands of excess deaths in the coming years—if not millions.“There is danger in the exuberant feeling of ever growing power which the advance of the physical sciences has engendered and which tempts man to try, “dizzy with success”, to use a characteristic phrase of early communism, to subject not only our natural but also our human environment to the control of a human will,” Hayek said. Dizzy with success in this age of wonders, Hayek feared humans would be bewitched by their accomplishments and believe they could achieve anything if they could only control society—”a striving which makes him not only a tyrant over his fellows, but which may well make him the destroyer of a civilisation which no brain has designed but which has grown from the free efforts of millions of individuals.” We witnessed firsthand in 2020 the fruit borne from this effort to control society to save it. There’s an important lesson in humility there, if humans are wise enough to see it. Source: fee.org
Published Date: June 30, 2021, 12:00 am
Post Comment
E-Magazine
RELATED Economics





